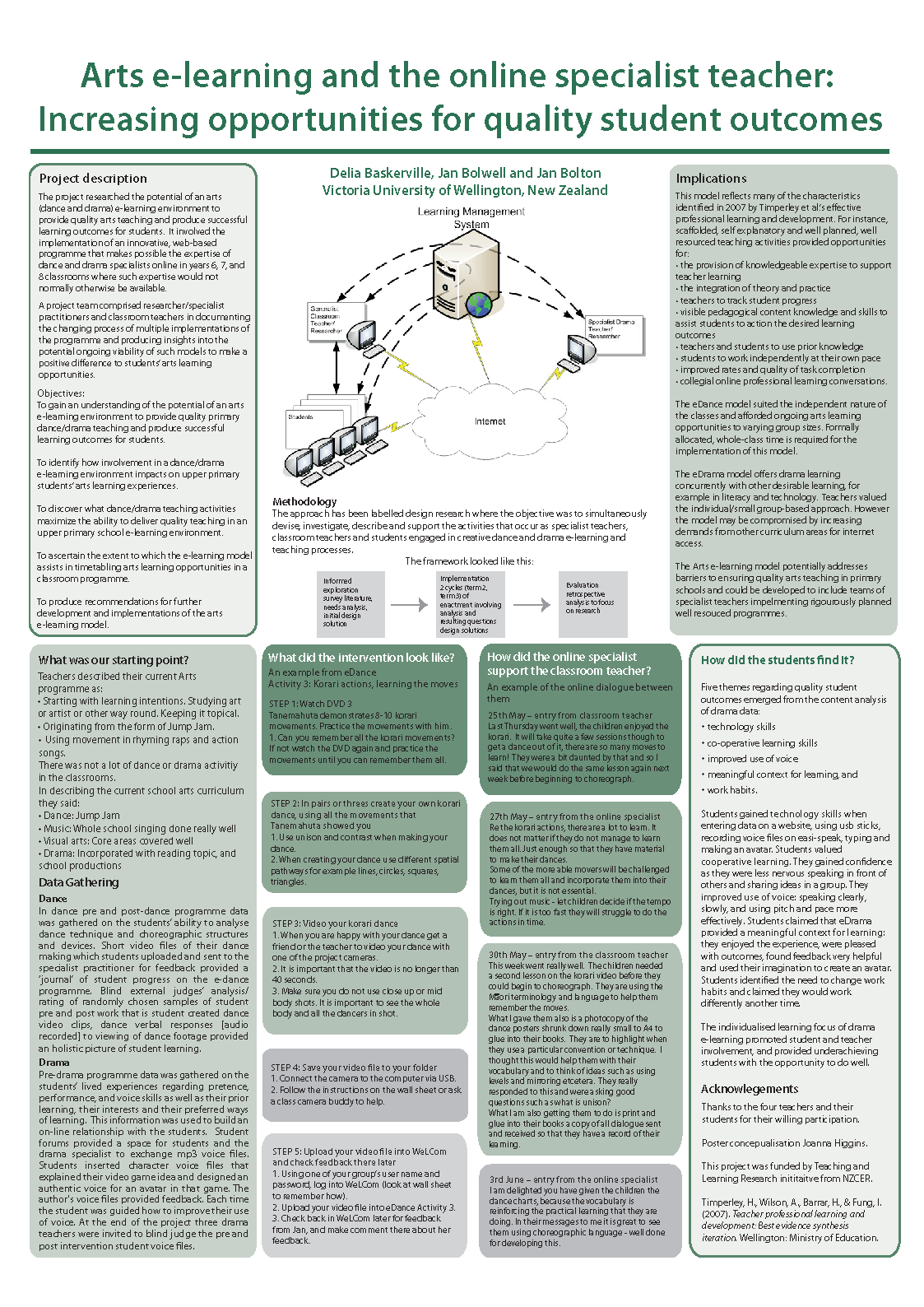
Using home languages as a resource to enhance statistical thinking in a multicultural classroom
Introduction Aotearoa New Zealand is a super diverse nation in terms of the ethnicities of its people and languages spoken. With an increased rate of immigration (New Zealand Immigration, 2018) from various parts of the world, the presence of multiple languages in many domains of social life is a reality. Individuals may identify with several nationalities or racial groups and may speak combinations or mixtures of several languages (Dockrell et al., 2022; Education Review Office, 2018). Consequently, classrooms are now places where learners have different linguistic and cultural backgrounds, where they may speak one language at home and another at school, where teachers and students may not share a common language