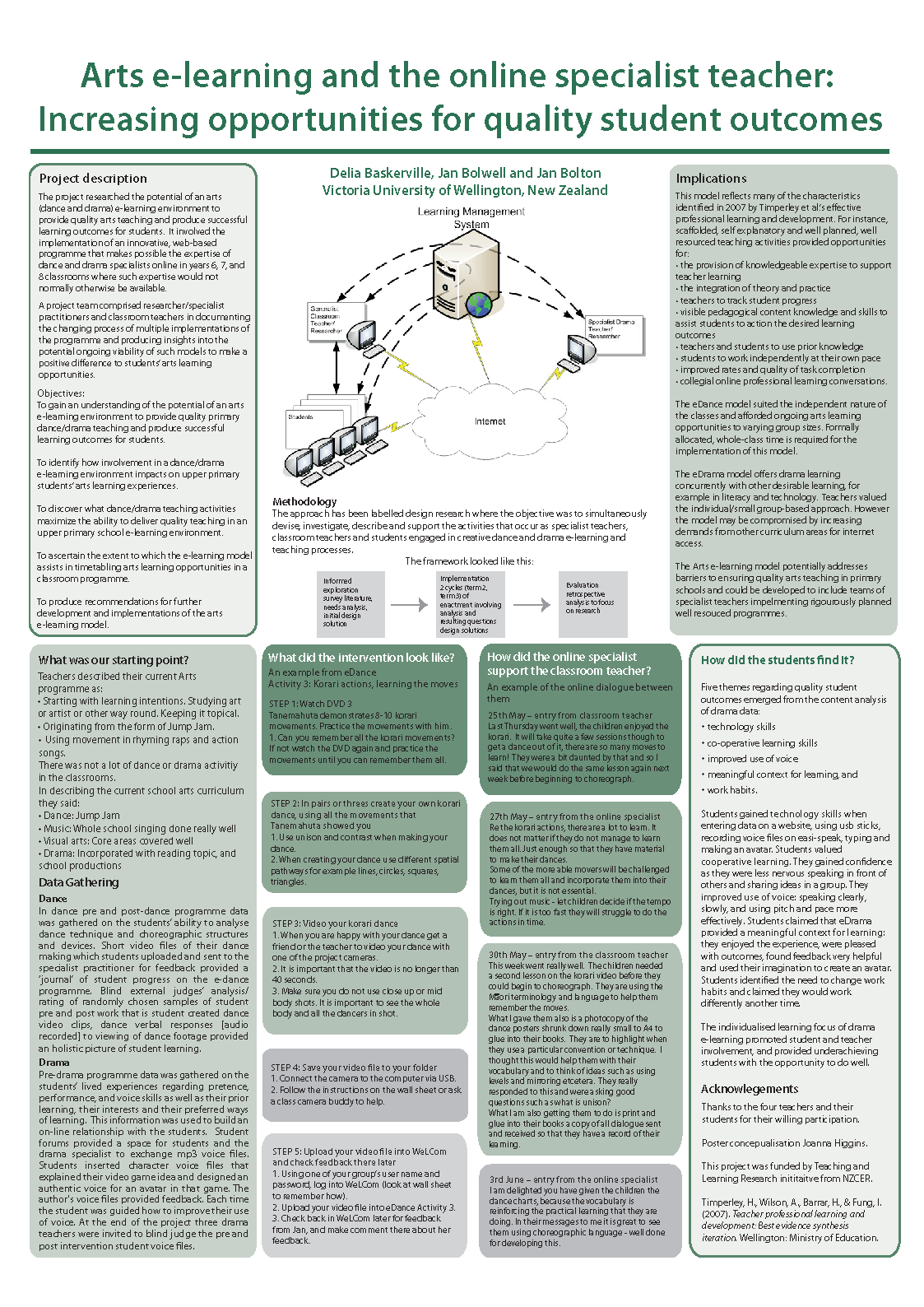
Moving a school: Higher order thinking through SOLO and e-Learning
Introduction Technological, social and economic change is encouraging increasing emphasis on the development of higher order thinking skills throughout the world and they are being incorporated into national curriculum goals in many countries, including New Zealand. Simultaneously the use of digital technologies is being promoted by many educators and authorities in this country and elsewhere as an approach that will enable students to develop these skills. An increasingly popular tool for identifying higher order thinking is the SOLO (Structure of Observed Learning Outcomes) taxonomy (Biggs & Collis, 1982). This taxonomy describes the complexity of student responses to questions or tasks, and also can be applied to the questions or tasks themselves.