The Apiscope Buzz: A mixed methods action research project investigating STEM to STEAM using the Apiscope as a tool for differentiated teaching and learning
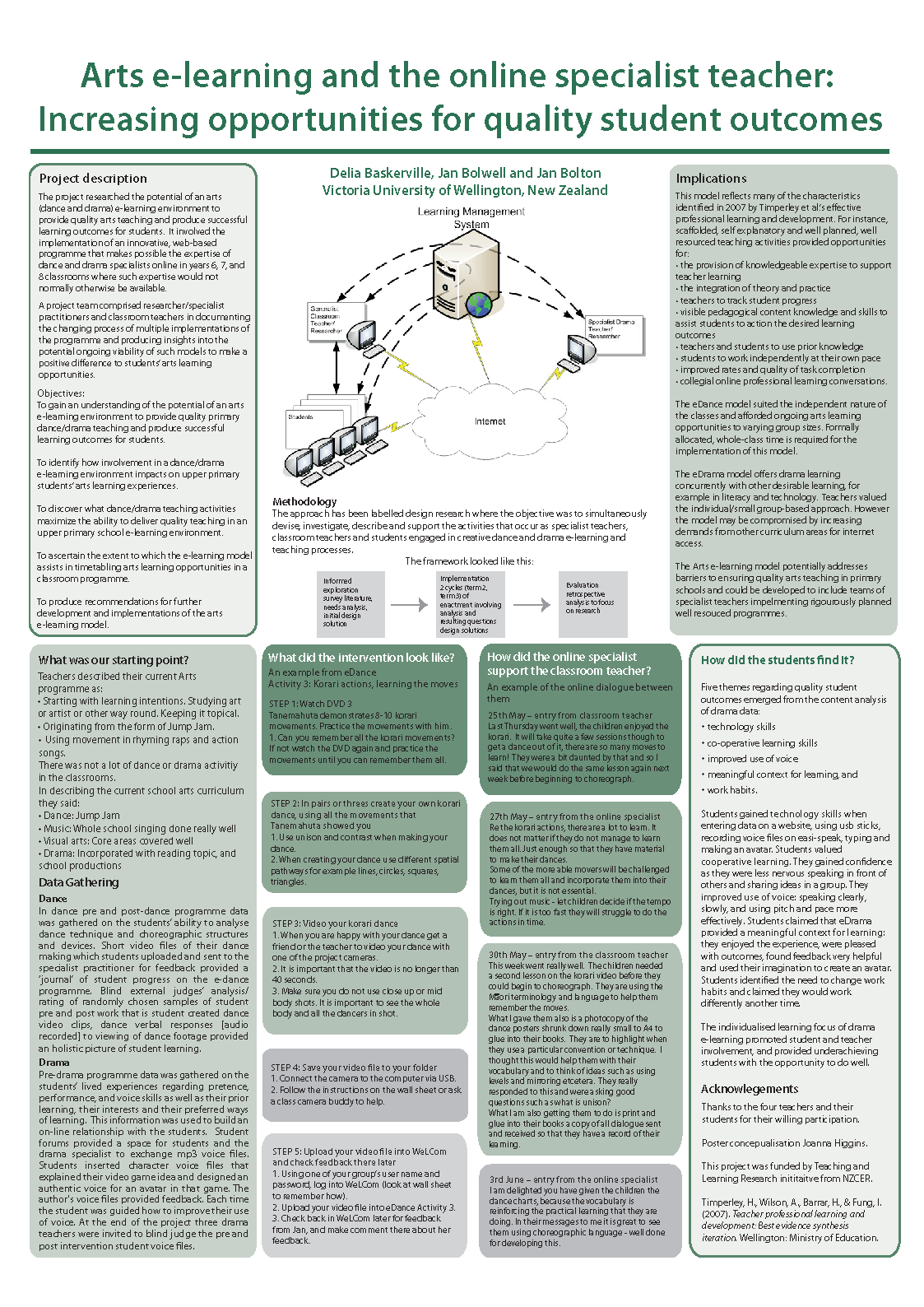
Introduction This Teaching and Learning Research Initiative (TLRI) project was a 2-year exploratory study focusing on differentiating the curriculum in response to individual learner differences. The project was designed to explore learning and teaching of differentiated scientific content through observational processes and the expression of that learning through the creative arts. This exploration was undertaken in two classrooms at Avalon Intermediate School and Newlands Intermediate School that were each provided with an observational beehive called an Apiscope. These observational beehives were central to the project, which explored how the study of bees can be used to facilitate the teaching of key concepts related to living systems—sustainability, work, survival, structures, patterns—that, in